|
Task Management Software |
 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
 TESTIMONIALS TESTIMONIALS
|
|
"...This is an excellent program. I'm so glad that I stumbled on to this when researching for task management programs. Very low learning curv, quite flexible, and the price is right. Tried at least 20 other programs, either too complicated, too expensive, or poor documentation..."
Chad Lindsey -
Honolulu, HI
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Project Audit checklist |
|
|
|
|
|
|

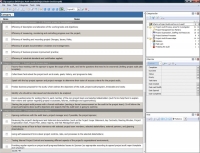 |
This Project Audit checklist will be helpful to those who would like to learn the purpose of this process and how the life cycle is organized. This checklist will explain what it is, how it is used, what activities it includes and what outcomes the audit is supposed to deliver in result
|
| Order 750 checklists in MS Word and PDF printable format at $49.99 USD only. |
BUY NOW!  |
What is a Project Audit and how is it used?
- Definition: This is an independent and pragmatic assessment (better conducted by an outside facilitator) of the project’s health. Its purpose is to uncover the issues, risks and challenges delivered by internal elements & external factors, which can affect the completion of the project, and to provide specific advice on how to bring the project back on track;
- Methodology: it is a process of analyzing project matters and elements to disclose reasons and underlying problems causing uncomfortable symptoms in project management. Project audit can considered as a super-sized project status capture with a purpose of detecting and rectifying issues, while they still can be fixed smoothly and economically. The following methods are used:
- Comprehensive review of all project documents including the project scope statement, project plan, project risk assessment, management of change, communication, etc;
- Meeting and interviewing all project team members (both individually and as a team);
- Meeting and interviewing the project sponsor, project stakeholders, and representatives of the organizational management who supervises the project team;
- Audit in project management helps the project manager, project sponsor and project team to get an adequate review of the project in order to identify what elements of the project were managed successfully and what were mismanaged, also what was poorly established and can be improved to avoid mistakes in the future, and to develop a better manageability;
- Reasons for the procedure: Change of the Project Manager (when previous one was replaced due to some reasons), Post-implementation review, Project is Trouble (Delivery issues, Complaints of the Customer, etc). Serious Changes in project’s structure;
Areas for investigation:
- Project Management Key Matters:
- Appropriateness, relevance and correctness of key matters stated in the Project Charter;
- Efficiency of the matters included into definition of the Project Scope (WBS, PBS, project’s outcomes, objectives, or deliverables, etc);
- Efficiency, clearness and completeness of the project requirements (Quality, Costs, Time);
- Efficiency of the Project Plan (its quality, appropriateness of details, validity, etc);
- Efficiency and regularity of the Project Plan reviews, changes, updates;
- Efficiency of reporting the working progress and comparing it against the Project Plan;
- Efficiency, clearness and completeness of the Project Financial Plan;
- Efficiency of project communications (with its sponsors and other stakeholders);
- Efficiency, clearness and completeness of Project Schedule (project milestones, deliverables, tasks, timeline);
- Reviewing and analyzing Risk Logs, Issue Logs, Change Logs;
- Reviewing and analyzing Project Management strategies and policies;
- Efficiency of rational decision-making;
- Efficiency of project documenting;
- Efficiency of the project management team’s skills and experience;
- Efficiency of the Project Office;
- Project Organization, Staffing and Resources:
- Efficiency of organizational & functional units and sub-teams;
- Efficiency of internal and external communications comprising the managerial interrelations, reporting, seniority, recruiting function, publicity;
- Efficiency of team structure and departmentalization;
- Efficiency and clearness of working responsibilities and roles;
- Efficiency of staff members’ skills, education and experience;
- Efficiency, clearness and completeness of the Project Resources Plan;
- Appropriateness of working facilities, technology and physical premises;
- Efficiency of tools and technology applied;
- Efficiency of accounting the working time of manpower & equipment;
- Efficiency of managing raw materials, warehousing, etc;
- Project Business Processes:
- Efficiency of description and allocation of the working tasks and objectives;
- Efficiency of measuring, monitoring and controlling progress over the project;
- Efficiency of handling and recording project Changes, Issues, Risks;
- Efficiency of project documentation circulation and management;
- Efficiency of business process improvement practice;
- Efficiency of industrial standards and certification applied;
Steps:
- Initiation:
- Face-to-face meeting with the sponsor to agree the scope of the audit, and list the questions that need to be answered (drafting plan template);
- Collect basic facts about the project such as its scale, goals, history, and progress to date;
- Speak with the key project sponsor and project manager to determine their vision of success criteria for the project audit;
- Finalize business proposal for the audit, which outlines the objectives of the audit, timescales and costs;
- Identify who should be interviewed and documents to be analyzed;
- Create questionnaires for sending them to each member of the core project team and selected stakeholders (such forms help them to explain their visions and opinion regarding project’s successes, failures, challenges and opportunities);
- Starting the process with a formal notification (sending a formal announcement on the audit to the project team). It will inform the project participants about audit’s objectives and aspects that the audit team is going to examine;
- Field work:
- Opening conference with the audit team, project manager and, if possible, the project sponsor;
- Reviewing the project’s background and historical documentation (such as the Project Scope Statement, key Contracts, Meeting Minutes, Project Organization chart, Project Plan, status reports, and Risk Management plan);
- Conducting series of face-to-face interviews with selected project team members, selected stakeholders, external partners, and gleaning observations;
- Giving self-assessment forms about project controls, risks, and processes...
| Order 750 checklists in MS Word and PDF printable format at $49.99 USD only. |
BUY NOW!  |
|





 |
CentriQS Tasks Management Solution 
Looking for multi-user task management software? Try CentriQS complete task management solution for planning, tracking and reporting tasks, projects, and schedules. Increase productivity of your small business or office by better organizing your employees' tasks and time.
 FREE Download CentriQS FREE Download CentriQS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CentriQS  -15% OFF -15% OFF |
All-in-one business management software
for small and midsize enterprises |
 |
|
|
| VIP Task Manager |
Multi-user project management software
to plan, schedule and track project tasks. |
 |
|
|
| VIP Checklists
|
More than 750 ready-to-use to-do lists
to plan your personal and business life |
 |
|
|
| VIP Team To Do List |
Professional task management software
to make and send team todo lists by email |
 |
|
|
| VIP Organizer |
Personal time management software
to organize time at home and at work |
 |
|
|
| VIP Simple To Do List
|
Simple and effective to-do list software
to plan daily chores, trips, wedding, etc. |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|